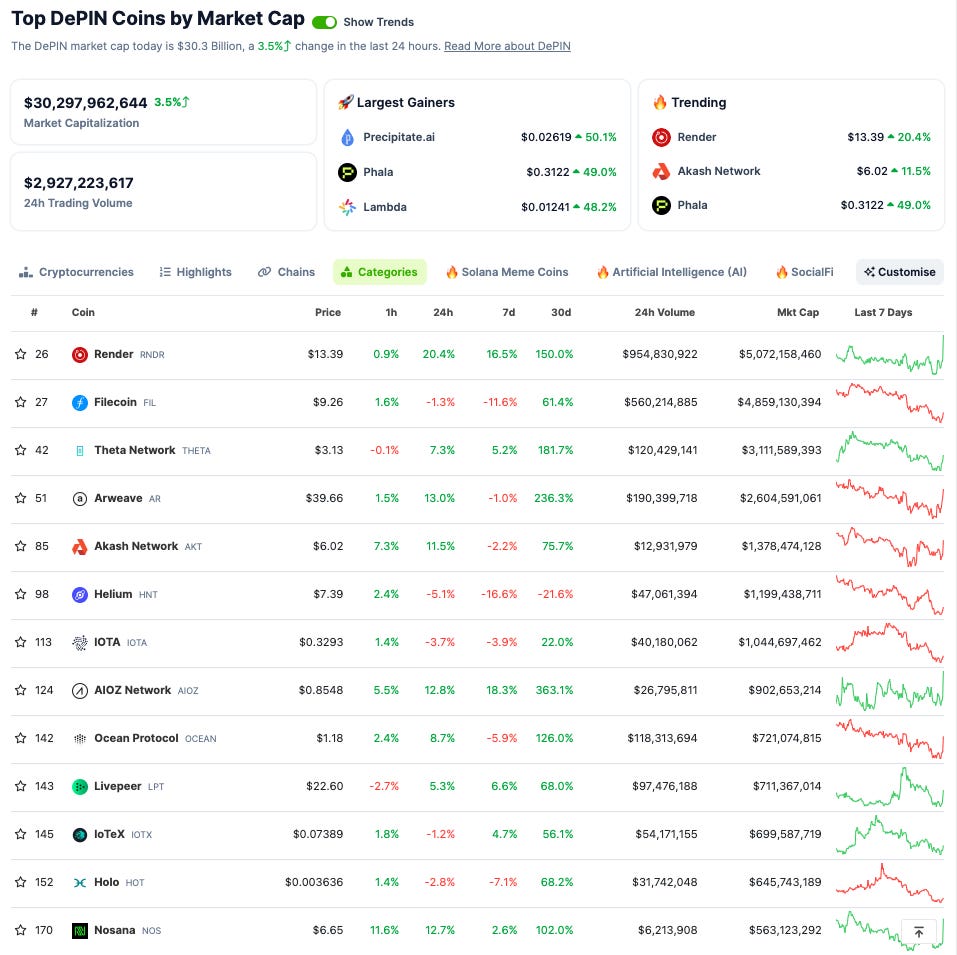
What Is DePIN? 🌐
Decentralised Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN) can change how we manage and use physical infrastructure. We explore components, benefits, challenges, and potential applications.
Hello, y'all. If you think you know your music, then this is for you frens. A complete go. Check out 👉 Asset - Music Nerd
This is The Token Dispatch 🙌 you can hit us on telegram 🤟
Decentralised physical infrastructure networks, or DePINs, are decentralised networks of interconnected devices that enable shared access to and management of physical resources through smart contracts, peer-to-peer protocols, and distributed ledger technology.
They allow for the creation of peer-to-peer networks of interconnected devices, which can be used to provide services ranging from cloud storage to autonomous transportation.
By creating a trustless environment for resource sharing and exchange, DEPIN promotes greater efficiency, sustainability, resilience, and community empowerment.
How It Works
At its core, a DePIN is a network of physical resources that are represented digitally on a blockchain.
Each resource is associated with a unique token, which can be bought, sold, or traded just like any other cryptocurrency.
Users who want to access a particular resource must first acquire the corresponding token, either through mining, purchasing, or trading.
Once they have enough tokens, they can use them to access the resource they need.
Example: A distributed cloud storage system built on top of a DEPIN. Each user who contributes storage space to the network receives a certain number of tokens based on the amount of space they contribute. Other users who want to store files on the network must first acquire some of those tokens. They then use those tokens to "rent" storage space from the network. The actual file storage and retrieval process is handled automatically by smart contracts, which ensure that everything runs smoothly and securely.
Components of DePIN
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): DLT provides secure, transparent record-keeping capabilities enabling real-time tracking, monitoring, and validation of transactions within the network. It ensures data integrity without requiring central oversight or control.
Smart Contracts: Automated agreements between parties encoded as self-executing algorithms on the blockchain govern interactions within the DEPIN ecosystem. They facilitate seamless exchanges of value and ensure equitable compensation based on predefined rules.
Interoperable Devices: IoT sensors, actuators, gateways, and other connected devices form the backbone of DEPIN networks. They communicate over standardised protocols, allowing them to share information and coordinate actions effectively.
Peer-to-Peer Protocols: P2P communication enables direct interaction among network participants, eliminating intermediaries and reducing transaction costs.
Token Economy: Cryptocurrencies or tokens incentivise participation, reward collaboration, and promote liquidity in DEPIN markets. Tokens also serve as a medium of exchange, facilitating frictionless transactions within the network.
Use Cases
There are numerous potential applications for DEPINs, spanning a variety of industries.
Distributed Cloud Storage: In a cloud storage system, users can rent out unused hard drive space in exchange for tokens. An alternative to traditional cloud storage providers, that rely on large, centralised servers.
Energy Grids: Blockchain-enabled peer-to-peer trading platforms allow prosumers (producers and consumers) to transact directly, fostering local energy markets and accelerating renewables adoption.
Transportation Systems: Autonomous vehicles integrated into shared mobility networks optimise traffic flow, enhance safety, and decrease emissions.
Water Distribution Facilities: Real-time metering and automated billing systems encourage efficient water use, detect leaks promptly, and prevent fraud.
Waste Management: Smart waste bins equipped with RFID tags monitor fill levels, trigger pickups only when necessary, and track recycling processes.
Benefits
There are several advantages to using DEPINs compared to traditional centralised infrastructure.
Decentralisation: Because DEPINs don't rely on a single point of control, they are less vulnerable to failures or attacks. If one node goes down, the rest of the network can continue functioning normally.
Scalability: As more users join a DEPIN, the network becomes larger and more robust. Unlike traditional infrastructure, which often requires significant upfront investment to scale, DEPINs can grow organically as needed.
Flexibility: DEPINs allow for greater customisation and adaptability than traditional infrastructure. Since users can choose which resources to invest in and how much to pay for them, they can tailor the network to meet their specific needs.
Security: Blockchain technology provides strong encryption and consensus mechanisms, making it difficult for malicious actors to tamper with or manipulate the network.
Transparency: All transactions on a DEPIN are recorded on the blockchain, making it easy to audit and verify activity. This can increase trust and accountability among participants.
Challenges
Despite their potential benefits, DePINs face several challenges that will need to be addressed before mass adoption.
Regulation: Regulatory frameworks for blockchain and decentralised technologies are still evolving, and it remains unclear how governments will approach issues such as taxation, liability, and consumer protection.
Interoperability: To achieve true widespread adoption, DePINs will need to work seamlessly with existing infrastructure and protocols. Ensuring compatibility across different platforms and standards can be challenging.
Usability: While blockchain technology has made great strides in recent years, it still suffers from usability issues that make it intimidating to non-technical users. Simplifying the user experience will be crucial for attracting mainstream adoption.
Performance: Decentralised networks tend to be slower and less performant than centralised ones due to latency and other factors. Improving performance while maintaining security and reliability will be key.
Decentralised Physical Infrastructure Networks represent an innovative approach towards managing critical resources more efficiently, sustainably, and inclusively. They hold immense potential to transform traditional infrastructure sectors. As the technology matures and regulatory frameworks catch up, we may see increasing adoption of DePINs in various industries, leading to a more equitable and resilient infrastructure landscape.
TTD Week That Was 📆
Saturday: HODL The Dip? 🙇♀️
Friday: Here we go again🩸👀
Thursday: Will Liquidity Crunch Hit Bitcoin? 🛢️
Wednesday: From $3,600 to $73,000 ⤴️
Tuesday: This Time Ethereum? ⏳
Monday: Bitcoin Flips Silver 🪙
TTD Week in Funding 💰
Berachain. $69 million. DeFi-focused, EVM-compatible Layer 1 built on the Cosmos SDK and powered by Proof of Liquidity Consensus.
MadWorld. $13 million. Post-apocalyptic NFT shooting game. Players collect and trade tokenised land assets based on real-world locations
TunaChain. $8.92 million. An EVM-compatible modular execution layer on Bitcoin.
If you like us, if you don't like us .. either ways do tell us✌️
If you dig what we do, show us love on Twitter, Instagram & Threads🤞
So long. OKAY? ✋